Skip to main content
SKILLS IN ORGANIZATIONAL STRATEGY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
- WHAT IS STRATEGY
- The way (hypothetically determined) an organization seeks to achieve the vision and mission.
- Contains
- Set of goals/objectives
- Distinct method involve people (who), resource (what) and process (how) used by an organization to compete with its competitors
- Specifies what you do and what you don't do
- Change=[Dissatisfaction.Vision.first step of action]>Resistance
- Change occurs when dissatisfaction, vision and first step of action exceed resistance
- Change means to move form one state to another to become different from what it was.
- Dissatisfaction used as a lever
- Change will happen when the product of D.V.F greater than R
- Resistance transfer into productive energy
- People get excited when they participated
- WHY DO ORGANIZATIONS NEED A STRATEGY?
- External positioning
- need to match internal resource and capabilities to the external environment to achieve sustainable competitive advantages arise from having capabilities for customers that competitors cannot offer
- Internal alignment
- resources are allocated to support strategic priorities and enable organizational units and employees to make decisions and implement policies that are consistent with achieving and sustain competitive advantage
- Johnson G & Scholes: the direction and scope of an organization over the long term, which achieves advantage for the organization through its configuration/resources within a changing environment and to fulfill stakeholder expectation
- Objective (similar to vision statement)
- the end of strategy is designed to achieve
- quantitative target and time frame
- Scope
- domain (niche) in which the enterprise intends to operate
- customer segment, product line breadth, technologies employed, geographic locations served/degree of vertical integration (value chain activities will perform)
- Advantage
- enterprise will achieve its objective
- enterprise do differently/better/uniquely compared to competitors
- values proposition company offer to attract customers
- strategy canvas/values curve (blue ocean strategy)
- WHAT IS STRATEGY
- broad business options and choices that have organization-wide impact. Always more than one way to achieve a vision/support a mission
- hypothesis of the best way for the organization to achieve its vision and mission and satisfy customers and stakeholders
- requires selection among alternative ways of doing things, focusing on few things and deferring/rejecting the rest
- can be long term or short term
- answer the broad questions
- different than tactics (answer more narrow questions)
- Ronda-Pupo & Guerras-Martin (2011): the dynamics of the firm's relation with its environment for which the necessary actions are taken to achieve its goals and/or to increase performance by means of the rational use of resources
- BENEFITS OF STRATEGIZING
- encourage forward thinking
- provide clear direction and objective
- facilitate allocation of resource
- facilitate internal communication & cooperation
- identify new opportunity for exploitation
- prepare for threats
- STRATEGY FORMULATION: mental process to create broad formula for how to compete
- COMPETITVE STRATEGY: about being different
- CATEGORIES OF STRATEGIC IDENTIFY/DIFFERENTIATION
- Cost leader-charge the same price as competitor/less but operating with lower costs (operational excellence)
- Differentiated Value Provider: operating with same cost as competitors but earning higher revenues by being able to charge higher price than competitors for customer who value their particular form of differentiation
- Customer intimacy: focus on customer relationships and experience as the central themes of decision making about the product and services offering
- Product leadership: strives to create best-in-class products, with an unbeatable combination of features, form and function
- Disruptive innovation: creates a new category of business/attract new category of customer, change the game to new playing field
- THE KEY QUESTIONS STRATEGY MUST ANSWER
- Where will we compete
- which market segment will we compete
- which customer will we serve
- what will we offer our chosen customers
- What do we want to achieve
- what is our aim
- what will be our measures of success
- How will we win
- for value creation for customer and investors
- What will be our key priorities
- how will we concentrate our scarce resource to achieve success
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT DEFINITION
- the identification of the purpose of the organization and the plans and actions to achieve the purpose
- set of managerial decision and action that determine the long term performance of business enterprise
- involve formulate and implement strategy that will help in align the organization and its environment to achieve organizational goals
- IMPORTANCE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
- give broader perspective to the employees of an organization
- employee can better understand how their job fits into the entire organizational plan and how it co-related to other organizational member
- employee become more trustworthy, committed and satisfied as they co-relate themselves very well with each organizational task
- understand reaction of environmental changes on the organization and the probable response of organization with the helps of strategic management
- employee can judge impact change of their own job and effectively face the changes. manager & employee do appropriate things in appropriate manner. need to be effective and efficient
- major role of strategic management is to incorporate various functional areas of the organization completely to ensure functional areas harmonize and get together well
- keep a continuous eye on the goals and objectives of the organization


- VISION
- statement that outline organization's long term aspirations and desired future state.
- should be motivating, challenging, inspiring and provide framework for decision making, goal setting and strategic planning
- consistent with an organization's mission and core values and reflects its strengths, capabilities and competitive advantages.
- communicated clearly and effectively to stakeholders, employees, customers, investors, community
- MISSION
- organization's purpose and reason for existence
- brief, clear and concise statement outline goal/objective of organization
- provide direction for decision-making, strategy and planning
- answers questions what organization does, who serves, how it serves
- reflect organization core values, beliefs, principles and understood by stakeholders, employees, customers, investors and community
- flexible enough to adapt to changes in organization's environment, goals and priorities
- CORE VALUES
- fundamental belief/principle deeply ingrained and important to an individual, organization, society
- guiding principles that helps to shape decision-making, behavior and actions
- can be moral/ethical principles, cultural values, beliefs about what is important/valuable/personal convictions
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT PROCESS
- Environment assessment
- PESTEL analysis:
- identify and analyze external factors that impact on organization's performance and success
- Political: taxation policies, trade restriction, political stability and government intervention
- Economic: inflation rates, exchange rates, economic growth and unemployment rates
- Sociocultural: demographics, lifestyle trends, consumer attitudes and social norms
- Technological: new inventions, automation, digitalization, research, development
- Environmental: climate change, natural disaster, pollution and sustainability concerns
- Legal: employment laws, consumer protection laws, intellectual property laws, health and safety regulation
- SWOT analysis
- strategic planning tool that helps individuals and organizations identify and evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
- Strength: skills, resource, competitive advantage
- Weakness: lack of resource, skills, expertise
- Opportunity: market trends, emerging technologies, new partnership
- Threats: competition, economic downturn changing regulation
- TOWS analysis
- suggest specific strategies that can be used to address the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
- Strengths-opportunities
- Weakness-opportunities
- Strengths-threats
- Weaknesses-threats
- Identifying enabler and pains
- Identifying stakeholder
- Strategy formulation
- vision & mission
- core values & customer value proposition
- strategic themes/thrust & result
- strategic objectives
- strategy map
- measures & targets
- strategic initiatives
- Strategy implementation
- Strategy monitoring & controlling
- Assessment & strategy review
- 9 STEPS TO SUCCESS BUILDING & IMPLEMENTING A BALANCED SCORECARD
- Assessment
- BSC development plan
- Strategic elements
- Communications & change management plan
- Evaluation
- results
- revised strategies
- Cascade
- business & support unit scorecards
- Automation
- software
- performance reporting
- knowledge sharing
- Initiatives
- Performance measures
- performance measures
- targets
- baselines
- Strategic map
- objectives linked in cause-effect relationship
- Objectives
- Strategy
- customer needs & value
- strategic themes
- strategic results
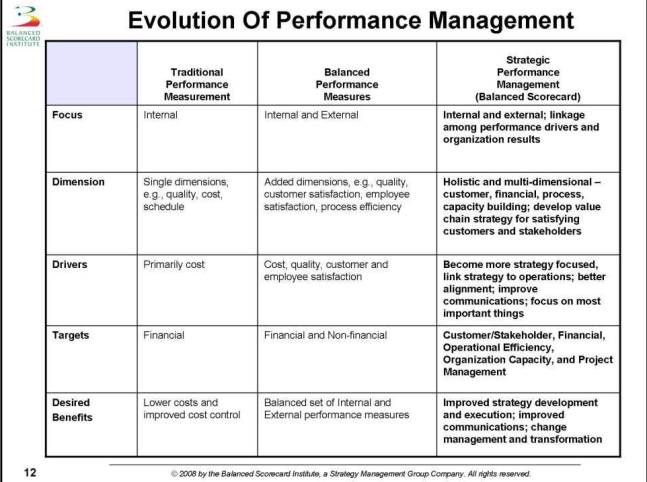
- WHAT IS BALANCED SCORECARD
- David P. Norton & Robert Kaplan (1992): method approach company seen in balanced way through chosen perspectives beyond financial measure
- Balanced:
To be able to see things from various dimensions or perspective
- Perspectives balances: 2-max (dependent on situation)
- Outcome: resultant effect of performance
- Performance driver: thing/factor that affect future performance
- improved strategic planning process
- change initiative for visualizing and communicating an organization's long term strategic intent
- objective: framework for breaking strategy into actionable components
- strategic management system: align day-to-day work to an organization's vision and strategy using strategic performance measures and strategic initiatives
- inform strategic budgeting, and allow organization to learn what works and to become more strategy focused
- LOGICAL MODEL COMPONENTS
- Input: resource used to produce output and outcome
- Process/activity: program does with inputs
- Output: products and service create/deliver
- Intermediate outcome: changes occurred in lives of beneficiaries/participants fallen short of significant benefits (attitudinal changes toward more civic participation)
- End outcome: changes occurred in lives of of beneficiaries/participants constitute significant benefits (increased civic knowledge, increased likehood to perform service)
- LOGIC MODEL BENEFITS
- communicate potential value
- clarify results trying to achieve
- identify key program elements that must be tracked to assess program's effectiveness
- make clear program premises and make visible stakeholder assumptions
- improve program planning and performance by identify ways to measure program success and areas for improvement
- STRATEGIC PERSPECTIVES
- Financial: results that business provide to stakeholders
- Customer: identify customer, market segments and value propositions
- Learning & growth: infrastructure, people, system, procedures
- Internal process: key internal process drive business

- BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
- WHAT IS BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
- reduce cost
- raise value innovation
- remove decrease
- increase and establish
- find new customer group
- APPLICATION
- services: increase buyer value
- processes: increase efficiency
- products: increase sales & profits
- FRAMEWORK & ANALYTICAL TOOLS
- visual awakening
- PMS map
- as is strategy canvas
- BEC/BUM
- visual exploration
- 3 tiers of noncustomers
- Tier 1 represents people who will soon become customers.
- Tier 2 represents those who are aware of your offerings but refuse to switch.
- Tier 3 is unexplored; these non-customers are unaware of your offerings.
- 6 path framework
- visual strategy creation
- 4 actions framework
- ERRC Grid
- to be strategy canvas
- visual strategy fair
- as is strategy canvas
- ERRC grid
- to be strategy canvas
- 10 ESSENTIAL PRINCIPLES OF STRATEGY
- commit fully to a define objective
- seize the initiative and keep it
- economize to mass resource
- use strategic positioning
- do unexpected
- keep things simple
- prepare multiple, simultaneous alternatives
- take indirect route to objectives
- practice timing and sequencing
- exploit success
- STRATEGIC THEMES BALANCED SCORECARD
- the main, high-level business strategies that form the basis for the organization's business model
- serves as focal point for development specific objectives, measures, targets and initiative across areas of organization
- customer intimacy
- understand needs and provide tailored options
- increase satisfaction, improve retention rates, expand customer reach
- operational excellence
- improve operational efficiency, reduce cost, increase productivity
- reduce cycle times, improve quality and optimize resource utilization
- innovation
- develop new products, services/process create value for customer and drive business growth
- increase number of new product launched, improve speed of innovation, foster culture of creativity and experimentation
- employee engagement
- create positive work environment attract, retain and motivate top talent
- improve employee satisfaction, reduce turnover and increase productivity
- financial performance
- profitability, revenue growth and cash flow
- increase sales, reduce cost and improve margins




Comments
Post a Comment